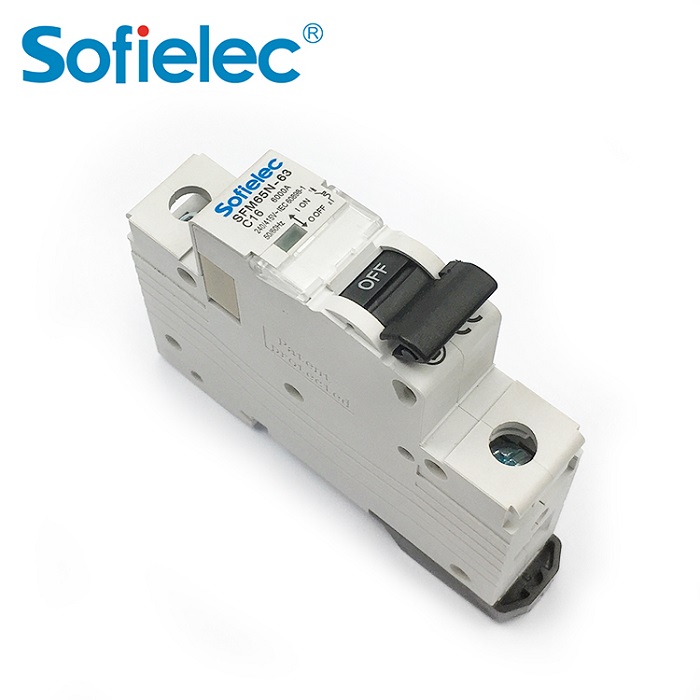
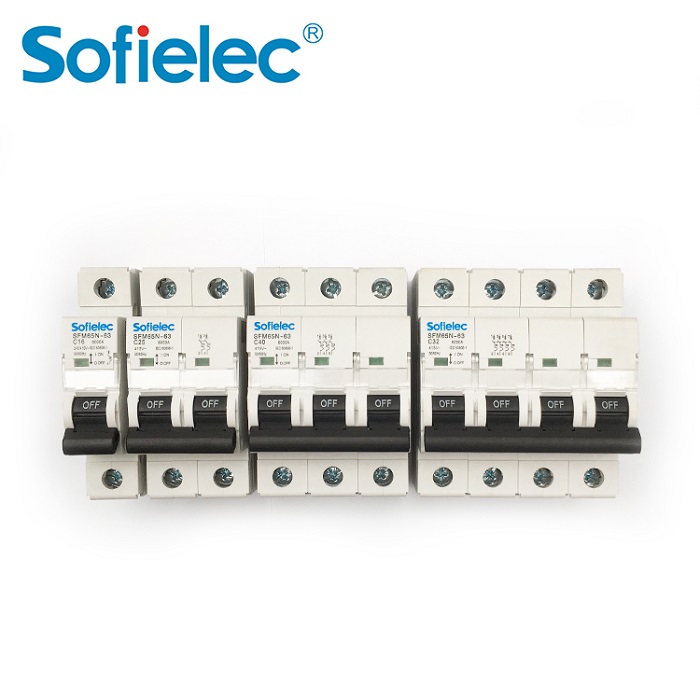
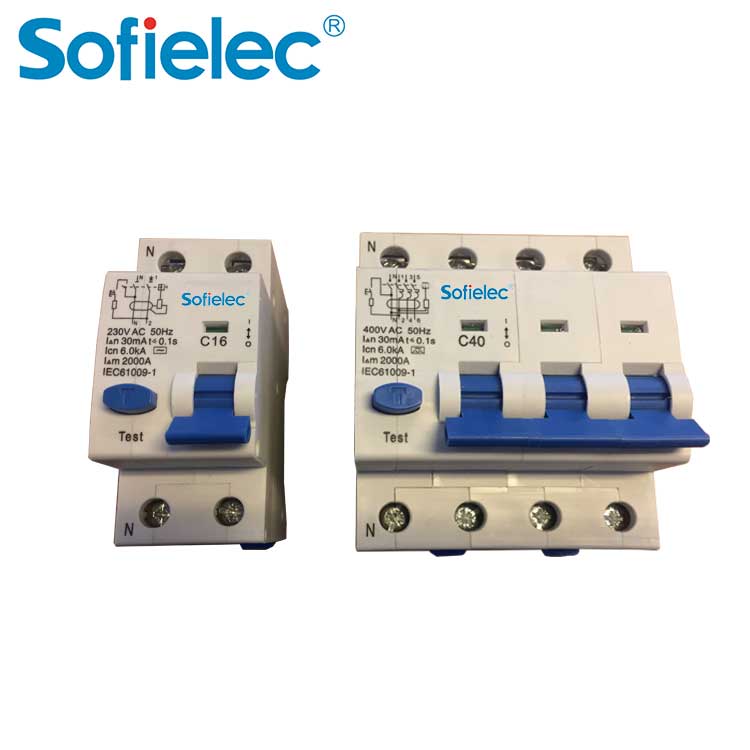
SFM65N-63 miniature circuit breaker has a high breaking capacity (6kA), mechanical life is 4000 times, and tripping curve is B, C, D, DIN guide rail installation.
MCB 6KA C25 Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker SFM65N-63 Parameter
| Categories | Economic 4.5KA, 6kA Regular Series Circuit Breaker |
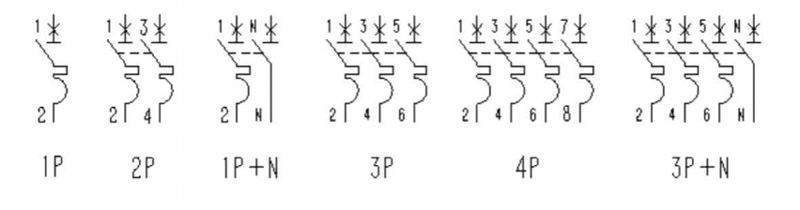
| Pole No | 1P. 1P+N. 2P. 3P. 3P+N. 4P |
| Rated current(A) | 1. 2. 3.4. 6. 10.16. 20. 25. 32. 40. 50. 63 |
| Rated voltage | AC 230. 230/400. 400 |
| Rated Frequency | 50/60Hz |
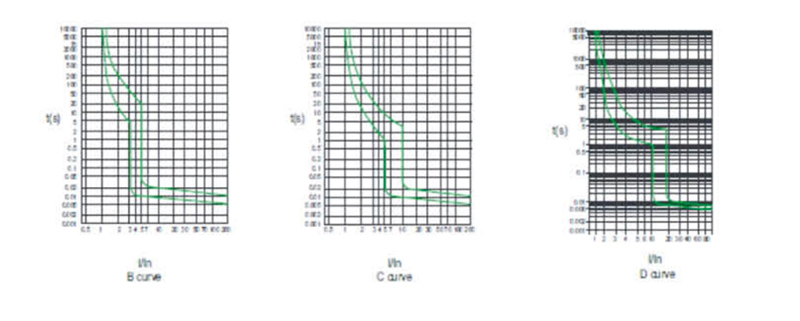
| Tripping curve | B. C. D |
| Rated short-circuit capacity (Icn) | 6000A |
| Mechanical life | 20000 times |
| Contact position | indication window |
| Degree of protection | IP20 |
| Connection terminal | Pillar terminal with clamp |
MCB 6KA C25 Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker SFM65N-63 Construction and Feature
■ Fine and unique appearance,advanced design
■ Short-circuit and overload dual-protection performance
■ High-breaking capacity (6kA) that is leading among the world similar products
■ Mechanical life:4000 times
■ Convenient and reliable installation
MCB 6KA C25 Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker SFM65N-63 Technical Data
■ Model: SFM65N-63
■ Rated current(A): 1、2、3、4、6、10、16、20、25、32、40、50、63
■ Rated voltage: AC 230.230/400, 400
■ Rated Frequency: 50/60Hz
■ Tripping curve: B,C,D
■ Rated short- -circuit capacity (Icn) :6000A
■ Mechanical life: 20000 times
■ Contact position indication window
■ Degree of protection: IP20
■ Connection terminal:Pillar terminal with clamp
■ Connection conductor: up to and including 16mm
■ Terminal Connection Height:H1=19.5mm,H2=21 5mm
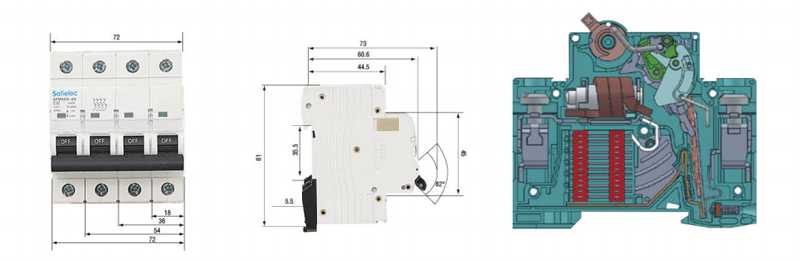
■ Installation:DIN-rail mounting
MCB 6KA C25 Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker SFM65N-63 Characteristic Curve
MCB 6KA C25 Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker SFM65N-63 Power Conumtion
| Rated current range(InA) | Max consumption/pole(W) |
| In<10 | 3 |
| 10 | 3.5 |
| 16 | 4.5 |
| 25 | 6 |
| 32 | 7.5 |
| 40 | 9 |
| 50 | 13 |
Wiring Diagram
Overload Current Protection Characteristics
| Test Procedure | Type | Test Current | Initial State | Tripping or Non-tripping Time Limit | Expected Result | Remark |
| a | B,C,D | 1.13In | cold | t≤1h | no trippint | |
| b | B,C,D | 1.45In | After test a | t<1h | tripping |
Current in the 5 s in the increase of stability |
| c | B,C,D | 2.55In | cold |
1s60s(In≤32A) 1s32A) |
tripping | |
| d | B | 3In | cold | t≤0.1s | no tripping |
Turn on the auxiliary switch to close the current |
| C | 5In | cold | ||||
| D | 10In | cold | ||||
| e | B | 5In | cold | t<0.1s | tripping |
Turn on the auxiliary switch to close the current |
| C | 10In | cold | ||||
| D | 20In | cold |
Overall&installation Dimensions
> What are the four types of timer switches?
A time switch, often simply referred to as a timer, is a device that automatically controls when an electrical circuit is turned on or off. It's like a programmable ...
> Can You Replace a 10 Amp Breaker with a 20 Amp Breaker?
Replacing a 10-amp circuit breaker with a 20-amp one without a thorough professional evaluation is extremely dangerous and poses a significant fire hazard. Let's ana...
> What Makes a Circuit Breaker Essential for Home Electrical Safety?
Home electrical safety ranks high on every homeowner’s priority list, yet many overlook the quiet workhorse that prevents crises before they start. This device acts ...
> What Scenarios Require the Use of a Residual Current Circuit Breaker?
Electrical safety is a top priority in daily life and work, yet many people are unsure when to use a device that guards against electric shock. This article explains...








